Knock Knee
Knock knee (also called "knock-knee deformity," "knock-knee syndrome," "knocked knee" or "genu valgum") is an incorrect alignment around the knee that can affect can people of all ages. Over time, the imbalance of force it places on the knees can cause pain, joint damage and early onset knee arthritis. Correction of the deformity will improve knee mechanics and walking capability, reduce pain and prevent a rapid progression of damage to the knee.
What is knock knee?
Knock knee is a condition in which the knees bend inward and touch or "knock" against one another, even when a person is standing with their ankles apart. This places excessive force on the outer side of the knee, which can cause pain and damage over time.
Knock knee is usually bilateral – affecting both legs – but in some cases, it may only affect one knee.
Are knock knees normal?
Temporarily knocked knees are part of a standard developmental growth stage for most children. This usually corrects itself as the child grows. Knock knees that persist beyond six years of age, are severe or affect one leg significantly more than the other may be a sign of knock-knee syndrome.
Most children experience normal angular changes in their legs as they grow. Children are typically bowlegged until they begin walking at around 12 to 18 months. By about twp to three years of age, their legs have usually begun to angle inward, making them knock-kneed. During normal growth phases, the child's legs will straighten out by age seven to eight.
Knock knees that remain outside of these normal developmental growth patterns may be caused by disease, infection or other conditions. If the angle of the legs from hip to foot falls outside normal patterns, worsens over time, or is present on only one side of the body, this suggests a person has a more serious form of knock knees, and further evaluation by an orthopedic specialist may be necessary. Surgery may be needed to treat the condition.
(Find a knock knee specialist at HSS.)
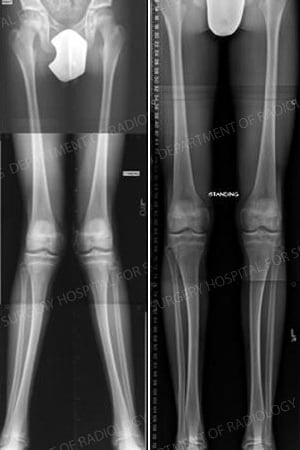
X-rays: (Left) preoperative image showing knock knee. (Right) postoperative image showing leg alignment after surgical correction and removal of metal plates.
What causes knock knee?
Knock knee can be caused by an underlying congenital or developmental disease or arise after an infection or a traumatic knee injury. Common causes of knock knees include:
- metabolic disease
- renal (kidney) failure
- physical trauma (injury)
- arthritis, particularly in the knee
- bone infection (osteomyelitis)
- rickets (a bone disease caused by lack of vitamin D)
- congenital (inborn) conditions
- growth plate injury
- benign bone tumors
- fractures that heal with a deformity (malunion)
Being overweight or obese can also put extra pressure on the knees and contribute to knock knee.
What are the symptoms of knock knee?
The most prominent symptom of knock knee is a separation of a person’s ankles when their knees are positioned together. Other symptoms, including pain, are often a result of the gait (manner of walking) adopted by people with knock knees. These symptoms may include:
- knee or hip pain
- foot or ankle pain
- feet not touching while standing with knees together
- stiff or sore joints
- a limp while walking
- reduced range of motion in hips
- difficulty walking or running
- knee instability
- progressive knee arthritis in adults
- patients or parents may be unhappy with aesthetics
A person may also have other symptoms from an underlying condition that is causing the knock-knee syndrome. In people of all age groups who have knock knees, one or both knees is abnormally overloaded. This excessive force can lead to pain, further bone deformity, knee instability and progressive degeneration of the knee joint. In particular, adult patients who have been knock-kneed for many years often overload the outside (lateral compartment) of the knee, and stretch the inside (medial collateral ligament – MCL). These forces can cause pain, knee instability (including complex patellofemoral instability) and arthritis.
How is knock knee diagnosed?
An orthopedic specialist will review the patient’s medical and family history, any pre-existing conditions and current health. They will also do a physical examination of the legs and gait. Standing-alignment X-ray or EOS images will help confirm the diagnosis. These are radiological images of the leg from hip down to the ankle, which help the doctor locate the exact location and mechanical axis of the deformity.
How is knock knee treated?
For mild cases of knock knee in children or adolescents, bracing may reposition the knees. When this does not work, or if the patient is an adult at the time of diagnosis, an osteotomy to realign the knee (usually in the tibia but sometimes in the femur, or both) is done to prevent or delay the need for knee replacement.
If knock knee is caused by an underlying disease or infection, that condition will be addressed before any orthopedic correction begins. Treatment for mild cases of knock knee in children or adolescents may include braces to help bones grow in the correct position.
If a gradual correction does not occur, surgery may be recommended. In the growing child, guided-growth minimal-incision surgery may be used to encourage the leg to gradually grow straight. Learn more from the articles and video below.
Video: HSS patient's knock-knee experience
Below, see a video on how HSS patient Bonnie gained improved mobility and emotional health through knock-knee correction, and explore patient case histories and before-and-after photos.
Other patient case histories
Knock Knee Success Stories
Medically reviewed by Austin T. Fragomen, MD
