Reasons for Shoulder Replacement - Surgical Guide to Right Total Shoulder Replacement
Estimates in 2013 show that over 50 million people were diagnosed with a form of arthritis, or “inflamed joint.”
Arthritis refers to a condition to any joint where there is damage to the smooth cartilage that covers a moving surface of a joint (articular cartilage). The damage eventually leads to cartilage loss , in the end stage resulting in “bone on bone” of the joint surfaces, and pain.
After the hip and knee, the shoulder is the third most common joint affected by arthritis. However, the loss of cartilage that characterizes shoulder arthritis is frequently a source of severe pain, limited function, joint stiffness, and significant diminishment in quality of life. While there is no cure for arthritis, there are many treatments, both non-surgical and surgical, that enable the symptoms to be addressed and for patients to maintain active lifestyles.
Types of Shoulder Arthritis
Osteoarthritis: This is called a “wear and tear” type of arthritis, that probably occurs from a combination of use, genetics, micro trauma, and increased forces across the joint. The cartilage loses its normal chemical makeup, becomes frayed and worn, and eventually disappears; without this protective covering, the underlying bones grind against one another causing pain. (See Fig. 4)
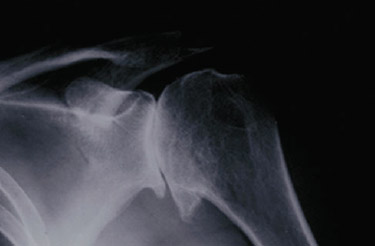
FIg. 4: X-ray showing osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint
Inflammatory arthritis: In conditions such as Rheumatoid Arthritis, multiple factors, often having to do with the immune system, lead to inflammation of the joint and joint lining, ultimately wearing away the cartilage surfaces. Fortunately, the medical treatment of many types of inflammatory arthritis have made tremendous advances, and the need for surgical treatment has greatly diminished.
Post-traumatic arthritis: This can result from a fracture of the ball or the socket in which the cartilage surface is damaged at the time of the bone fracture. Eventually, this damage can cause the cartilage surface to wear out and disappear.
Symptoms
As with other joints, the most common symptom of shoulder arthritis is pain with activity. In time, pain can occur at rest. As the cartilage disappears, the joint becomes stiff, reducing range of motion and limiting activity. Often this can interfere with even the most common tasks of everyday life, such as dressing, reaching for objects, and even personal hygiene. As joint motion is lost, tasks such as driving, athletic activity, housework, and even writing and computer work can be affected. The pain is frequently centered on the back of the shoulder, but commonly is felt all the way down the arm to the elbow.
Perhaps the most disabling symptom for most people is the loss of sleep, as it frequently becomes difficult to find a comfortable position either on the affected or unaffected side.
Motion is often severely affected, and it may be accompanied by cracking, grinding, or catching (crepitus) as the ball/socket bones rub against one another.
Shoulder Injuries
Cuff tear arthropathy: This is the end stage of very large tears of the rotator cuff tendon which is a union of four muscles that are the stabilizers and the primary movers of the shoulder joint. While large tears of the rotator cuff tendon are uncommon, an estimated 4% of patients with untreated rotator cuff tears develop cuff tear arthropathy. Treatment of shoulder arthritis caused by cuff tear arthropathy can be particularly difficult, since it results from damage to both soft tissue support of the joint, as well as the joint surface. (See Fig. 5)
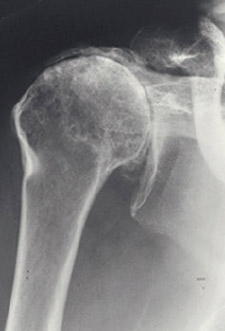
Fig. 5: X-ray showing both arthritis and large tear of rotator cuff tendon
Osteonecrosis (Avascular necrosis):This is an unusual condition in which the blood supply to the bone forming the ball of the shoulder is interrupted, leading to the death and collapse of a segment of the bone. With loss of the bone support, the overlying cartilage is subject to forces which cause the cartilage to become damaged as well.
